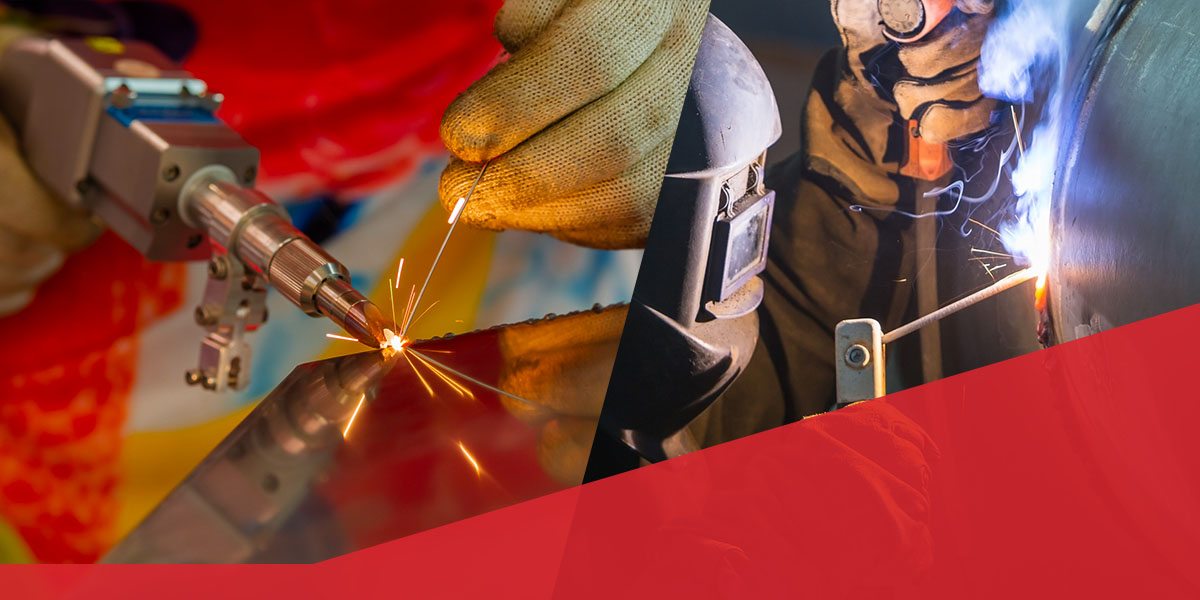
Manufacturers across various sectors turn to handheld laser welders for faster production cycles and flexible workflows. Traditional welding methods still have their place in various applications, but handheld systems offer industrial-grade capabilities to a wide range of shops.
Learn about the difference between handheld laser welders and traditional welding.
Understanding Handheld Laser Welding
Handheld laser welding uses a high-energy laser beam to accurately fuse materials. The system features a fiber laser source, which generates a focused, stable beam delivered through a fiber cable to a handheld welding head. This configuration creates a controllable, small heat-affected zone while producing strong, clean welds. The concentrated beam enables quick, repeatable welding.
Benefits of Laser Welding
Handheld laser welders deliver several performance and operational advantages that support production efficiency:
- High speed: Laser welding moves quickly because the beam delivers energy right where it's needed. When less material needs to heat up and cool down, the weld forms faster. This shortens cycle times for repetitive sheet metal jobs.
- Superior precision: Because the beam remains narrow and stable, you can work with tight seams and delicate geometries. The laser welding process maintains localized heat input, which helps prevent burn-through on thin metals.
- High-quality results: Laser welding produces smooth, clean seams. The lower heat input reduces warping, ensuring the finished part maintains its shape reliably. Jobs that require surface cleanup or grinding after welding can move straight to the next step.
- Versatility: Handheld laser welders work across a wide range of metals, from stainless steel and carbon steel to aluminum and galvanized materials. With parameter adjustments, you can shift between penetration welding or fine edge seams.
- Portability and ease of use: The handheld head easily reaches tight spots and large assemblies. You can also train new operators in hours, which helps teams maintain quality when staffing levels or experience vary.
Considerations of Laser Welding
Despite its numerous benefits, there are some considerations to keep in mind, including:
- Initial investment: The up-front price of a handheld may be steep because of the laser source and internal optics. However, you may see the investment balance out through faster cycle times, reduced rework and less post-weld cleanup.
- Safety considerations: Laser systems have protective features to guide safe operations, but the beams can reflect off certain surfaces. It's important to use proper eyewear and follow designated weld-area procedures.
Understanding Traditional Welding
Traditional welding is common due to proven metal joining capability and familiarity among experienced operators. The most common methods include:
- Gas tungsten arc welding (TIG) produces high-quality welds with excellent control, making it ideal for thin metals, but it is slower and more skill-intensive.
- Gas metal arc welding (MIG) provides good speed and is easier to learn, often used in fabrication shops and production lines.
- Shielded metal arc welding (stick) is tolerant of dirt and outdoor environments, making it suitable for use in construction and field repairs.
Benefits of Traditional Welding
Traditional welding still offers advantages, including:
- Lower entry cost: Traditional welding remains accessible due to the lower cost of the machines and consumables. For occasional tasks or small production runs, a conventional welder fits the need.
- Suitable for rough conditions: Stick welding is well-suited for outdoor work or heavy structural repairs, making it ideal for jobs with fluctuating conditions.
Considerations of Traditional Welding
Traditional welding's limitations become clearer when comparing it with laser welding:
- Slower process: Traditional welding introduces more heat into a material, and that wide heat-affected zone slows progress. You may need to frequently pause or adjust to maintain weld quality on thin metals. This pace creates challenges when you're trying to increase throughput or reduce lead times.
- Operator skill: Producing consistent results with traditional welding requires experience. Torch angle, travel speed, hand coordination and arc length can affect operations. Training helps, but the learning curve remains longer than with laser systems.
- Material distortion: Because the process heats a larger area, parts can warp or lose shape as they cool. Distortion also affects forming or fitting, which adds extra time to the correction process.
- Post-weld cleanup: Arc welding often leaves spatter or oxidation that requires grinding or brushing, which adds labor and extends production time.
The Difference Between Handheld Laser Welders and Traditional Welding
Comparing the two technologies helps clarify where each fits best in a manufacturing workflow.
Welding Speed and Efficiency
Laser welding moves up to four times faster than TIG because the beam heats only the exact point where the metal joins. With less heat spread, the metal reaches its fusion temperature more quickly and cools faster.
Traditional welding requires more time because the arc heats a larger section of the workpiece. You may also need to pause to control distortion or maintain consistency. As a result, laser welding tends to support higher throughput when you're managing tight production goals or looking to reduce bottlenecks in fabrication lines.
Precision and Weld Quality
The tight beam of a laser provides controlled penetration and a narrow heat-affected zone. That control helps you produce smooth, uniform seams that often require little to no refinishing. When parts must maintain exact shapes or when the aesthetics of the weld are important, laser systems provide reliable results.
Traditional welding is capable of strong, durable joints, but the broader heat input can introduce variation in sensitive materials. This means that arc-based results may require more surface preparation or finishing to achieve the same level of refinement.
Ease of Use
Handheld laser welders feature preset and user-defined modes, which reduce the amount of technique needed to produce a clean joint. While operators still follow proper procedures, the machine's controls handle much of the stabilizing work. This helps new operators gain confidence quickly and enables teams to achieve consistent results.
Traditional welding requires more manual skill. As a result, shops with rotating crews or limited training time may find laser equipment easier to integrate into their daily operations.
Applications of Handheld Laser Welders and Traditional Welding
Handheld laser welders and traditional welding each have strengths that suit specific tasks.
Applications of Handheld Laser Welders
Handheld laser welding excels in jobs requiring precision and speed, including:
- Sheet metal fabrication: Thin-gauge stainless panels and aluminum housings are ideal for handheld lasers. The localized heat input minimizes warping, allowing parts to retain their shape and fit together cleanly during assembly.
- Automotive components: Laser welding produces consistent seams for body and interior metal parts.
- Aerospace assemblies: Lightweight alloys and other aerospace parts require exact dimensional tolerances. Laser welding provides a narrow heat-affected zone, which reduces distortion and helps manufacturers maintain tight specifications.
Applications of Traditional Welding
Traditional welding remains a reliable choice in variable environments, including:
- Heavy structural construction: Thick steel frameworks and large machinery components respond well to arc welding. The process provides deep penetration and strong joints that withstand stress.
- Fieldwork repair: Equipment maintenance and outdoor projects often occur under less-controlled conditions. Arc welding performs consistently when exposed to rugged surfaces.
- Low-volume or mixed jobs: Workshops with variable production requirements may benefit from traditional welding methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some common questions about handheld laser welders versus traditional welding.
Is Laser Welding Better Than Traditional Welding?
In many cases, laser welding surpasses traditional welding because it offers remarkable speed, precision and low heat input, which makes it suitable for various applications. It produces cleaner seams and shortens cycle time.
What Kind of Routine Maintenance Does a Handheld Laser Welder Require?
Handheld laser welders benefit from routine checks that keep the beam stable and optics clean. Regularly inspecting and cleaning the protective lens helps maintain beam clarity. Additionally, monitor the cooling systems for temperature stability and proper flow.
Integrate a Handheld Laser Welder Into Your Workflow
Handheld laser welders help move parts through your workflow quickly and with minimal touch-ups. Alternative Parts, Inc.'s LightWELD laser welder and cleaner is easy to clean, quick to set up, and can handle various metals and thicknesses with adjustable power up to 1,500 watts. Our optimized presets reduce training time, and the integrated cleaning function lets you manage pre- and post-weld preparation with ease.
Our sales desk is staffed by people who understand welding applications and can help you select the right configuration. We offer expert guidance, backed by years of industry experience and factory-trained technicians.
Request a quote today to discover a faster and cleaner way to weld.